Authors: Alexandra Groome and Rachel Kastner. This interview originally published on Regeneration International
Authors: Alexandra Groome and Rachel Kastner. This interview originally published on Regeneration International
Ever thought about starting a business or building a career in regenerative agriculture? Prepare to get creative—and to get some dirt under your fingernails.
Ethan Soloviev is a founding team member of Terra Genesis, an international regenerative design consultancy. He helps create resilient and profitable businesses by redesigning supply chains to make them regenerative.
How did Soloviev find his way to his current career? Let’s just say that the guy who in his early 20s traveled the world to study apples, didn’t exactly follow a linear career track.
In this interview with Regeneration International, Soloviev covers several topics related to regenerative agriculture, including what types of experiences you might want to get under your belt if you’re contemplating a career in the fast-growing field of regenerative food, farming, and natural products.
This interview has been edited for brevity and readability.
Regeneration International (RI): Tell us about yourself.
Ethan Soloviev (ES): I’m a designer at Terra Genesis International. We grow the field of regenerative supply by working with companies around the world to transform supply chains into networks of resource production. I am also the EVP of Research at HowGood, which rates the sustainability of food, personal care products and cleaning products. We’re working to change the overall direction of the marketplace, and also to empower consumers to purchase and choose the best products that they can.
RI: How did you build your career in regenerative supply networks, agriculture and design?

ES: It’s been 15 years now. I did a degree in biology and afterwards I traveled around the world studying apples. I visited some amazing places—Sweden, Kazakhstan, Japan, New Zealand, Chile, Central America—and I got to see a global picture of how apples are grown. That really woke me up to agriculture and the damage that monoculture chemical industrial agriculture systems around the world are doing. That led me to permaculture. I took a Permaculture Design Course (PDC) and started a permaculture business back in 2005. I grew that business (AppleSeed Permaculture LLC) for a decade. It’s still one of the largest Permaculture Design businesses in the northeast of North America.
We started doing small-scale edible landscapes and eventually built up to larger design work, doing 300-1200-acre farms. I learned a lot about farm design and startup. People would often say, “It’s great to create food forests and ponds and biointensive vegetable gardens but it’ll take time, investment and energy to get this going—can it really make a return?” So we started running the numbers. We schooled ourselves very quickly in agronomics, and built a series of enterprise budgets to check if an enterprise was going to be economically viable. We found that a lot of the brilliant ideas of permaculture need to be checked against the economic reality of whatever place you’re working in to see if there’s something that can be sustained beyond the initial excitement.
RI: Right, the big question in the regeneration movement right now is “how do we scale regenerative agriculture?”
ES: It’s interesting, I go back and forth about whether “scaling” regenerative agriculture is the right thing to do. Part of me really wants to do it and wants to do it as fast as possible. It’s early and we’re heading towards the birth of a new industry. The supply of regenerative goods and massive landscape restoration that regenerative agriculture enables can produce multiple forms of profit. So it is exciting to think, “How fast can we scale this?”
However, another part of me has a different perspective. Regenerative agriculture is not a machine. We’re actually seeking to regenerate whole living systems. All of the language in the startup and venture capital communities is derived from a mechanical paradigm, where “scaling” means adding more machines to do more of the same work. Humans, and landscapes, are not machines. So I don’t think “scaling” is the appropriate metaphor for regenerative agriculture.
At the same time, I think now is a moment when we can and should work to quickly grow the community. How can we reconcile the two perspectives?

RI: What are the biggest gaps in knowledge in the movement right now that young people looking to get into the industry could fill?
ES: The biggest gap is investable enterprise —enterprises that have proven business models that actually capture carbon in the soil, increase biodiversity and generate financial capital returns. Proven business models and experienced teams will be required to metabolize the slow money and venture capital that is out there looking for a place to land.
Most of what I see in the regenerative movement is big ideas and excitement but not a lot of reality about how to pull off those ideas. That’s another big gap. There are many things that we can do to create enterprises worth investing in. Whether we’ll see exponential or linear or logarithmic growth, I’m not sure, but I do believe that working with the current system ofaccepting investment capital is going to be the fastest route to move forward and set the foundation for the real birth of a new industry.
The movement needs people who have depth of knowledge in what they’re doing. We need people who have experience running and growing businesses, or who want to go and get that experience. Even more, we need people who can do the farming. People who can actually get out there and run a holistic management livestock operation with multiple species on multiple pieces of land, who can successfully repair the land and grow food. We also need people with experience growing nut trees and fruit trees—perennial crops have already proven to be profitable, and they are our best bet for rapid global carbon sequestration. Then we need to integrate the two, bring together livestock operations and perennial tree crops—that’s where the fun really starts.
RI: For people who don’t have that in-depth knowledge or experience, where should they start?
ES: People would do well to hone in on what they’re really excited about. If it’s nut crops, great! Go for that. If it’s animals, great! Go for that. If a number of people can get depth in these functional farming enterprises and collaborate with other people who have gone and acquired the business skills along the way, that will lead to the creation of new enterprises. We could call this integrative depth. We’re really going to need teams of people working together to move regenerative agriculture forward.
I think we need about 1000 companies to really take this on. The restraint and challenge with that right now is that there are only about 10 businesses that have even said that they want regenerative supply systems. Those companies are great. Some of them are large and moving in this direction quickly. But they aren’t enough.
The 1000 companies need to be a combination of 1) existing companies who agree to pick up and take on regenerative agriculture, transform their supply systems into regenerative supply, and 2) new ventures with totally fresh perspectives, drawing from fresh investment sources.
RI: What is TGI doing to get those other 990 companies on board? And how does that relate to developing your client base?
ES: Terra Genesis focuses primarily on the natural products industry—food, consumer packaged goods and cosmetics. The exciting thing for our clients is there’s actually a real business case for regenerative agriculture. We carry out risk assessments where we look at a company’s supply chain, which includes all of the ingredients in their portfolio whether it’s 5 or 500. Then we ask, “What are the risks right now?” “What are the opportunities?”
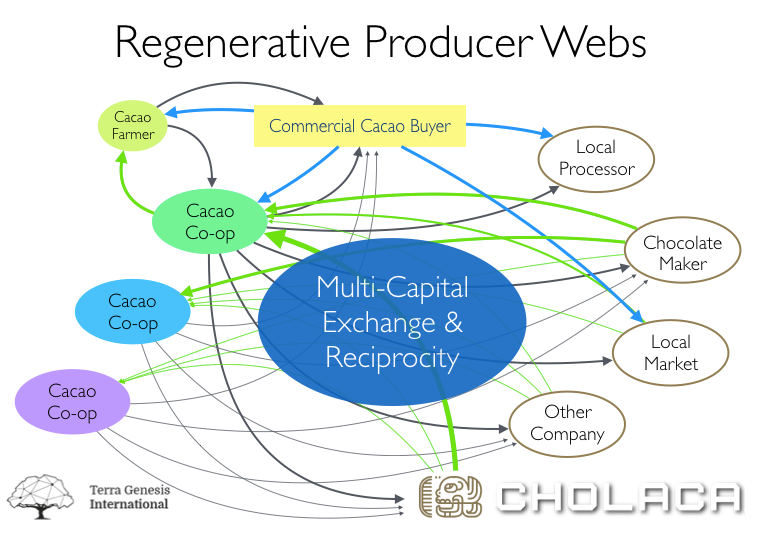
A lot of times the opportunities come from where a company is purchasing from of the commodities marketplace, whether it’s cocoa butter or citric acid or almonds. We hone in on those and look for ways to go directly to producers who are really pushing the edge on regenerative practices. By cutting out the multiple middle-people that are implicit in the commodity supply chain you can get prices that are similar or even better, while simultaneously offering real living and cultural capital profits on the ground for farmers. There are actual cost saving potentials in doing this inside a supply chain! And then we help our clients leverage the story of doing this.
Businesses that take a step in this direction, especially now, they get to be leaders. They’re early adopters and they will fully shine at the top. Patagonia, Nutiva, Lush Cosmetics and Epic are all talking about regenerative agriculture. They have real leadership in the marketplace.
Fortunately there’s a lot of room in a lot of different categories for businesses to step up and head towards regenerative agriculture.
RI: Which categories have the most potential right now?
ES: Cosmetics. Cleaning products. Sunscreen. Clothing. In food, there are so many opportunities! I don’t think there’s a potato chip company that is doing regenerative agriculture yet. How about an ice cream company? Tea. Soda. Almonds. Any kind of fruit. Olive oil. Salt. Bread. Beer. In any category brands are always looking for ways to position themselves as #1 (that’s one of the immutable laws of marketing). I think regenerative agriculture is a powerful tactic for this—it almost creates a new category for brands to step into and lead.
RI: What are your top favourite design courses that you recommend, to help people build the right skills to work in this industry?
ES: If you’re new to this realm, take a Permaculture Design Certification (PDC). You can do that while working your job that you don’t really like, at a bank or at a software company or wherever. The reason I say that is that while it is useful to grow and build skills in certain practices, what’s more useful if you want a career in regeneration is to evolve your paradigm. To do this, you have to disrupt your current paradigm. The PDC will do that. PDCs are an emersion in ecosystem thinking and whole systems design. Go get the certification. It’s a great start.
The next level of depth I recommend is taking a REX course from Regrarians, which is really the best training in regenerative agriculture that’s out there. In the past our team has run Carbon Farming Courses, and we’ll be re-starting some carbon farming education later this year. Also excellent would be any trainings in holistic management, from Savory Institute, or Holistic Management International. They’re different, but both are good.
RI: After taking some of these training courses, what next?
ES: Go work on a farm. You need to actually work, and then ideally manage a perennial agriculture or an agroforestry or a livestock-based system. If you’ve got a great idea and are trying to go out there and pitch people on it and get venture capital to fund an idea, unless you have proven experience and a proven business model, it’s not really going to work.
Go get some experience! Dig in. Spend a year or two on the farming side of things actually farming and producing food or fiber. You could also explore growing crops for the personal care industry. There’s something very interesting about growing for personal care: the margins are much better than they are in food. And for single ingredients (e.g. essential oils or nut butters), if you’ve got a really good story, then you can gain leadership and sales.
L’Oreal has a plan to be carbon negative by 2020. It’s one of the five largest personal care companies in the world. They’re going to need to be purchasing fair trade regenerative agriculture products in order to achieve that goal. But there’s not enough supply for that anywhere on the planet. Maybe 1/1000th of it currently exists. So get to work!
RI: What about supply chain management courses or MBAs to complement on-the-ground experience?
ES: I’m a big fan of on-the-job learning and training. There’s one masters degree I highly recommend, from Gaia University. It’s a global action learning system that encourages people to be working at their jobs while learning and getting accredited while they do it. You could for example do an online supply chain optimization course while working for a personal care or food products company, and get credit for it.
As for an MBA, while I’m not 100 percent sure, I’m going to go ahead and say, “yes.” We need some people who are excited about regenerative agriculture to go get an MBA and report back on how useful it’s been. As we discussed earlier, I think there’s a danger in getting addicted to the “scale or die” mechanical model so popular in current business. It looks nothing like how natural systems actually work. Make sure to take your PDC as you do your MBA. Or volunteer on a local organic farm every weekend to keep it real. If there’s anybody who’s got an MBA who wants to play in this realm, let’s go for it, I’d love to talk to them and hear their experiences. I haven’t seen MBA graduates turn into leaders of regenerative enterprises or regenerative agriculture systems (yet). But I would love to!
There’s an upswell of venture capital seeking to invest in regenerative enterprises but I don’t think there’s enough farm businesses that are ready. I think this asymmetry of demand and supply has emerged partially because it’s easier to invest money than it is to farm. Overall, I think the abundance of capital is a good thing. I see it as an activating force in this whole situation. For example, Renewal Funds, Cienega Capital, Cycleffect are doing excellent work to grow the field. There’s also a handful of family offices that are investing in some of the few regenerative agriculture enterprises that are ready for investment. So there are examples to learn from and work from… but still a ways to go.
RI: What kind of resources people should prioritize studying?
ES: Dirt and trees. Chickens and cows. Spend time in forests. Follow the closest stream to the top of the watershed. Those are really the best “resources.”
Online resources are great for quickly getting content and gaining intellectual capital, but what’s more important is taking the intellectual capital and grounding it into experiential capital. I stopped going to organic farming conferences four years ago because I realized I had gathered more intellectual capital than I had put into use. When I can really and truly say that I’ve put everything I’ve learned into practice, then I’ll go back for more.
That said, there is a difference between gathering informational content and growing your ability to vision, design and execute. There is always room for growth in these realms—especially if we are aiming to regenerate whole living systems. To work here, you need to engage in a community of practice. Ideally, it’s one that can disrupt your current paradigm and help you evolve a new one. And then disrupt your paradigm again.
RI: What “communities of practice” do you recommend?
ES: There are two communities of practice that are effective in this realm. The one I’m closely linked to is the Carol Sanford Institute and the Regenerative Business Summit. Carol Sanford is an incredible mentor and guide and she’s been working in this realm for four decades. Her lineage coined the term “regenerative” more than 40 years ago and put it to work inside companies like Procter & Gamble, Colgate Palmolive and Clorox. She’s now working with companies like Google on whole-systems paradigm shifts. Her school is amazing. Joining is by invitation only. You’ve got to make a real human connection with someone who is in the school. Being part of the school is not easy. It’s disruptive, intellectually confronting and definitely not a “comfortable” experience. That said, I would be happy to talk with anyone who wants to learn more.
There is also a simpler path. If you are the leader of a business and you want your company to be one of the 1000 that will move the world, then you can apply to come to the Regenerative Business Summit. It happens every year, in the fall, in Seattle. It’s an amazing event to get a sense of what a new paradigm of work looks like, and feels like. If you want an effective path towards regenerative business, this is a good place to start.
The other group that I recommend is Regenesis. They offer a series called “The Regenerative Practitioner,” which leads to connection with an international community of practice that’s putting the regenerative paradigm to work. It’s more focused on design, architecture and development but there’s great learning you can get there that can be applied to regenerative agriculture.
If you want to head into business, check out the Carol Sanford Institute and Carol Sanford’s books, especially for case studies. The Responsible Entrepreneur and the Responsible Business actually should be called the Regenerative Entrepreneur and the Regenerative Business but the publishing company (many years ago) basically thought that nobody would know what the word means… so they’re called “Responsible” but they’re really about regeneration. They’re the best books out there on the subject.
RI: I remember being introduced to Regenesis in Mexico City last year. They ask you to commit to attend several workshops, at least four.
ES: It’s an amazing group, definitely worth attending—but as I said, not necessarily “easy.” It’s important to commit over time, because regeneration takes a while to get going. It takes some time to disrupt your paradigm so that you can step into a new one. It takes some disturbance in a landscape for a the soil to start holding water and growing trees and really regenerating. Just going to a one-off workshop, you may get some inspiration. Reading a bunch of things on the internet, you may get some cool ideas. But committing to a school of practice that’s actively working on regeneration is a whole different world.
RI: One of the feasible ways to scale up or help the movement grow is to help others replicate frameworks that are working. Is TGI thinking of doing that, of helping other people do what you’re doing?
ES: TGI is definitely growing and adding new clients and team members rapidly. If you want to come engage, let us know. Formal education to train other consultants to do what we do doesn’t really make sense yet. I could see that potentially happening in the future. If anyone is interested in learning how TGI is working with clients, contact us and we’ll look for an opportunity where there’s space to play. Anybody can always come work with us if they bring a client.
I want to push back against the idea of “replicating” as a goal. This stems from that same perspective of a mechanical paradigm. TGI doesn’t do the same work with any client, ever. Every business is a unique business that has its own essence that we reveal. Nobody else has it. And if a company can use that, grasp it and work with it, then they become non-displaceable in the marketplace. There is a process that we use that has internal coherency from one client to the next, but it isn’t “replication”. Part of regenerating whole living systems is that, like real natural systems, you never do the same thing twice.
RI: It’s really skills for facilitating businesses through a process.
ES: Yes, but no. Do you know what the root word of facilitate is?
RI: Facil. To make easy.
ES: We don’t always make it easy for our clients. Making it easy isn’t always the right thing to do. Of course we have to “facilitate” from time to time, but our main work is more in what we call “resourcing.” Resourcing is supporting businesses and executives to re-source themselves: To become the source of their own fresh thinking. This is not based on trends in the marketplace or customer surveys. Using whole living systems frameworks, they develop their own image of what’s emerging in the world and how to head in that direction. That is not an easy process. People don’t like doing it.
Most businesses aren’t willing to do the hard work it takes to be regenerative.
When TGI works with a company we ask them to commit for three to five years. It takes that long to break out of old ruts and really disrupt and innovative. Like the personal growth and development we discussed before, it requires commitment over time.
RI: Any closing words you’d like to add?
ES: You originally asked “how do you find a career in regenerative agriculture?” You can’t. They don’t exist. You have to go make them. And that means you’re either, 1) growing an integrative depth of experience in particular area that you have connection to and real commitment for and then start your own company, or 2) figuring out how to contribute value to an existing business that is heading in that direction.
RI: Anything else?
ES: Let me just make a quick note about NGOs and nonprofits. They’re great, there are lots of them and there are more NGOs talking and thinking about regeneration than there are businesses currently—for example Kiss the Ground, The Carbon Underground, Carbon Drawdown, Savory Institute, Soil Carbon Coalition, Green America, Biodiversity for a Livable Climate, International Living Future Institute, Holistic Management International, Regenerative Agriculture Foundation, Rodale and of course Regeneration International. All these organizations are doing excellent work and we partner with them wherever appropriate. That said, TGI has the belief that business is the most effective route through which large systemic world changes can occur. Therefore, we focus on business.
So… go get that integrative depth! Join a company that’s headed in this direction or start your own.
The key is not to focus on the “practices” of regenerative agriculture, but instead to disrupt, shift and evolve your paradigm and continue to do that in an ongoing way. If we have enough people doing it and taking their own unique paths to do it, then we can head towards the 1000 companies we need focused on regenerative agriculture.
When we do that we’ll be well on our way to birthing a new industry, and that’s really what I think is the bigger direction here for anyone interested in having a career in regenerative agriculture. We have to think big and beyond what’s currently there and work together, intensively, quickly to make it real.
Learn more:



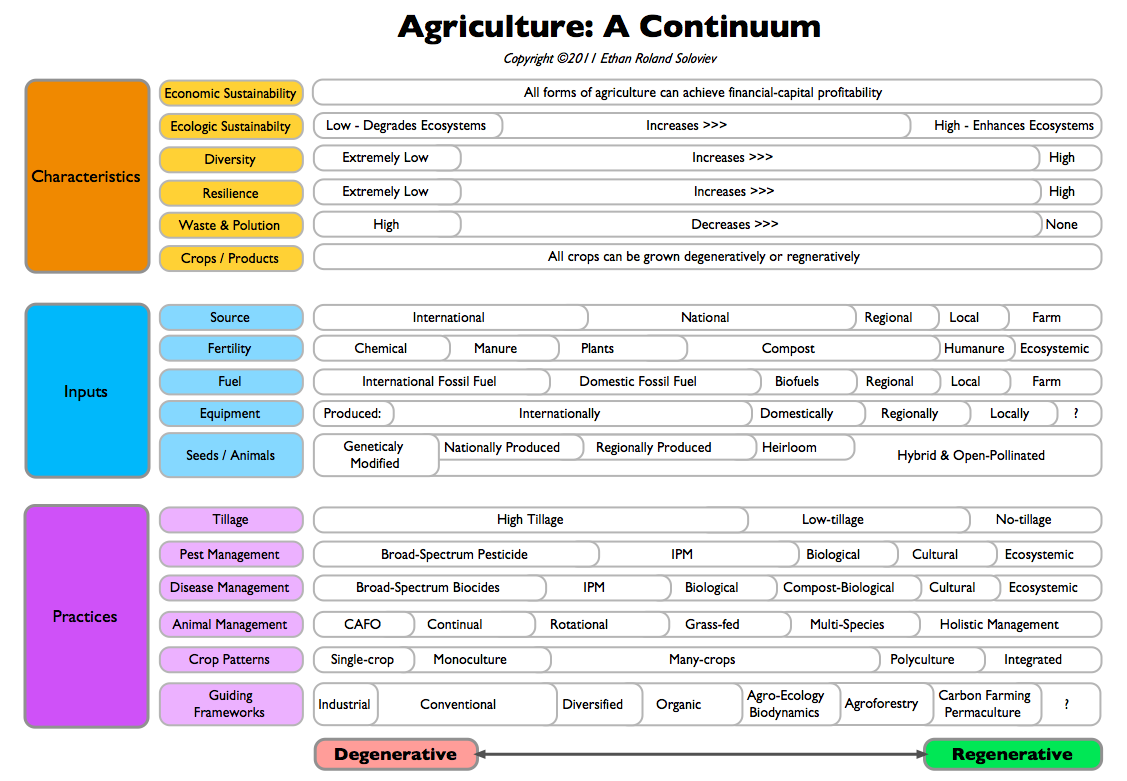
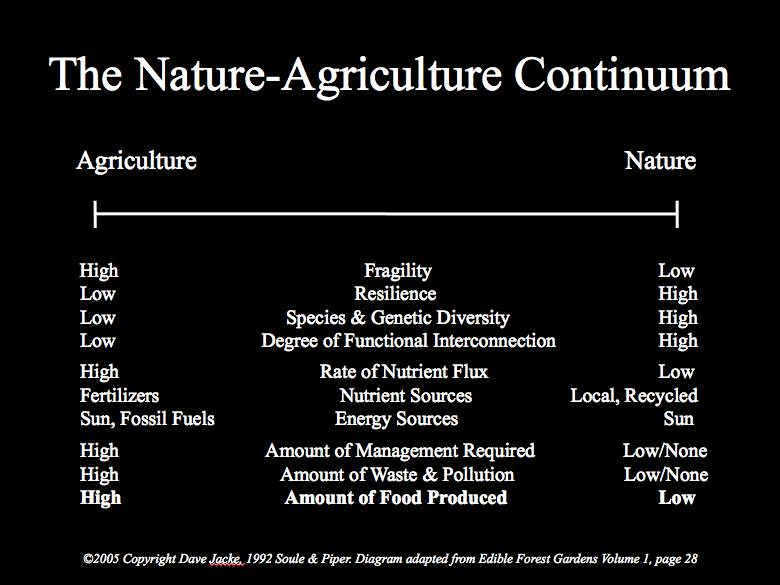
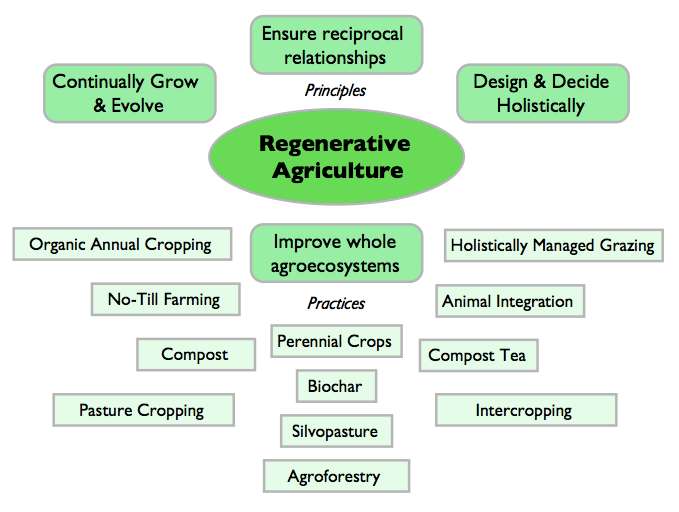
 On the other end of the continuum is “regenerative.” Here the vitality of a farm, a community, or a watershed is on-goingly developed and enhanced. The capacity and capability of the place or entity evolves, growing its complexity, interconnectedness, and ability to express its uniqueness into the world. New potential emerges that has never been seen before.
On the other end of the continuum is “regenerative.” Here the vitality of a farm, a community, or a watershed is on-goingly developed and enhanced. The capacity and capability of the place or entity evolves, growing its complexity, interconnectedness, and ability to express its uniqueness into the world. New potential emerges that has never been seen before.